Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку для подготовки студентов к интернет-тестированию Уфа 2007
| Вид материала | Учебно-методическое пособие |
СодержаниеGeography and climate Plant and Animal Life Largest cities |
- Учебно-методическое пособие Санкт-Петербург 2001 удк 681. 3 Бобцов А. А., Лямин, 1434.37kb.
- Название работы, 564.65kb.
- Учебное пособие Для подготовки к тестированию Новочеркасск 2007, 2155.67kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Криминалистика», 121.72kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Эконометрика», 503.64kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Психология и педагогика», 723.57kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Международное, 422.1kb.
- Методические указания по выполнению семестровой контрольной работы с комплектом заданий, 701.46kb.
- Учебное пособие по английскому языку для студентов экономистов. Автор-составитель Большакова, 15.76kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Финансы», 513kb.
Languages
The United Kingdom does not have a constitutionally defined official language. English is the main language (being spoken monolingually by more than 70% of the UK population) and is thus the de facto official language.
The other indigenous languages are Scots (which is closely related to English) and the Insular Celtic languages (which are not). The latter fall into two groups: the P-Celtic languages (Welsh and the Cornish language); and the Q-Celtic languages (Irish and Scottish Gaelic).
Welsh is spoken by about 20% of the population of Wales, giving it around 600,000 speakers. Welsh speakers - particularly concentrated in neighbouring English counties and in London and other large cities.
Scottish Gaelic is spoken by roughly 1% of the population of Scotland. Lowland Scots is spoken by 30% of the Scottish population (approximately 1.5 million speakers).
In Northern Ireland, about 7% of the population speaks Irish and 2% regional forms of Scots. Alongside British Sign Language, Irish Sign Language is also used.
Cornish is spoken by roughly 3,500 people.
Recent immigrants, especially from the Commonwealth, speak many other languages. The United Kingdom has the largest number of Gujarati, Hindi, Bengali, Urdu, and Punjabi speakers outside of Asia.
Vocabulary notes
British Sign Language - Британский язык жестов (кинетическая речь)
Celtic language – кельтский язык
Cornish language - корнуоллский, корнийский язык
Indigenous – местный, туземный
Insular – островной; мягкий (об островном типе климата); замкнутый, сдержанный; ограниченный
Monolingual – одноязычный
Scots - шотландский диалект; шотландский; относящийся к шотландскому диалект
Scottish Gaelic – шотландский гаэльский язык (язык шотландских кельтов)
Welsh language - валлийский язык
Religion
Although today one of the most "secularised" states in the world, the United Kingdom is traditionally a Christian country, having official faiths:
Anglicanism, in the form of the Church of England, is the Established Church in England. The Queen is Supreme Governor of the Church of England.
Presbyterianism (Church of Scotland) is the official faith in Scotland.
The Anglican Church of Wales was disestablished in 1920.
The Anglican Church of Ireland was disestablished in 1871.
Other religions followed in the UK include Islam, Hinduism, Sikhism, Judaism, and Buddhism.
The UK still is a predominantly Christian country. This is reflected throughout British public life – for instance there is an established church in England and a national church in Scotland. The Head of State is a Christian monarch crowned by an Archbishop in Westminster Abbey. British society could be said to belong to the Judaeo-Christian tradition, and even though only 7% of people in the UK are actually practicing Christians, the majority of people in the UK, 72%, identify themselves as Christian. Over 75 % of UK citizens consider themselves to belong to a religion.
Each of the four nations of the United Kingdom has distinctive church traditions.
Vocabulary notes
Anglicanism - англиканское вероисповедание; англиканство
archbishop - архиепископ
(to) disestablish - отменять устои, основы, нечто основополагающее; отделять церковь от государства
Presbyterianism - пресвитерианство
(to) secularize – секуляризовать, делать светским, отделять церковь от государства
G
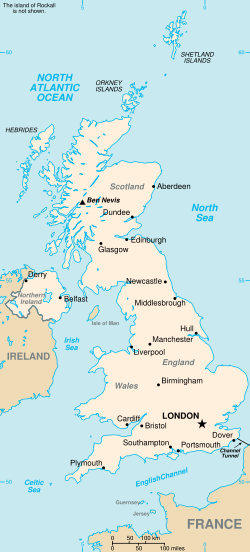
eography and climate
The United Kingdom lies to the north-west of the continent of Europe with the Republic of Ireland as its only land border. It extends over all of the island of Great Britain and the north-east part of the island of Ireland.
The United Kingdom is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean, and its bodies of water, including the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, St George's Channel, and the Irish Sea. The United Kingdom is linked to France and Continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel.
Most of England consists of rolling lowland terrain, divided from more mountainous terrain in the north-west (Cumbrian Mountains of the Lake District), north (the upland moors of the Pennines and limestone hills of the Peak District) and south-west (Exmoor and Dartmoor) by the Tees-Exe line. Lower ranges include the limestone hills of the Isle of Purbeck, Cotswolds and Lincolnshire Wolds, and the chalk downs of the Southern England Chalk Formation. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber Estuary. The largest urban area is Greater London. England's highest mountain is Scafell Pike, which is in the Lake District 978m. (3,208 ft).
Scotland's geography is varied, with lowlands in the south and east and highlands in the north and west, including Ben Nevis, the highest mountain in the British Isles at 1,344m. (4,406 ft). There are nearly eight hundred islands in Scotland, mainly west and north of the mainland, notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands. In total, it is estimated that the UK includes around one thousand islands.
Wales is mostly mountainous, the highest peak being Snowdon at 1,085m or 3,560 ft above sea level. North of the mainland is the island of Anglesey.
Northern Ireland is mostly hilly. The province is home to one of the UK's World Heritage Sites, the Giant's Causeway, which consists of more than 40,000 six-sided basalt columns up to 12m. (40 feet) high. Lough Neagh is the largest body of water in the British Isles, by surface area (388 km²).The highest peak is Slieve Donard at 849 metres (2,786 ft) in the province's Mourne Mountains.
The greatest distance between two points on the UK mainland of Great Britain is 1,350 km (839 miles) between Land's End in Cornwall (near Penzance) and John O'Groats in Caithness (near Thurso), a two day journey by car. When measured directly north-south it is a little over 1,100 km in length and is a fraction under 500 km at its widest.
England has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round, though the seasons are quite variable in temperature. However, temperatures rarely fall below −4 C and will only rise above 32 C in the height of the summer. The prevailing wind is from the southwest, bringing mild and wet weather to England regularly, from the Atlantic Ocean. It is driest in the east, warmest in the southwest in winter (closest to Atlantic currents), and warmest in the southeast in summer (closest to the European mainland). Snowfall can occur in winter and early spring, though it is not that common away from high ground.
Wales's climate is alike in most regards to that of England.
The climate of Scotland is temperate and oceanic, and tends to be very changeable. It is warmed by the Gulf Stream from the Atlantic. However, temperatures are generally lower than in the rest of the UK. Rainfall varies widely across Scotland. The western highlands of Scotland are the wettest place.
The whole of Northern Ireland has a temperate maritime climate, rather wetter in the west than the east, although cloud cover is persistent across the region. The weather is comparatively unpredictable at all times of the year, and although the seasons are distinct, they are considerably less pronounced than in interior Europe or the eastern seaboard of North America.
The United Kingdom can sometimes be affected by blocking highs during summer, and along with the rest of Europe, has been hit by severe heat waves in recent years.
Vocabulary notes
blocking high - блокирующий антициклон
Chalk down - меловая возвышенность, холм
Highlands - Северное нагорье, Северо-шотландское нагорье (северо-запад Шотландии; главный город - Инвернесс [Inverness]; там, в отличие от Шотландской низменности [Lowlands], дольше преобладал гэльский язык и гэльская культура ) полн. Scottish Highlands или Highlands of Scotland
Hilly – холмистый
Limestone – известняк; известняковый
Lowlands - Шотландская низменность (район центральной Шотландии в долинах рек Форт и Клайд) полн. Scottish Lowlands или Lowlands of Scotland; низменности
mainland - континент, материк; большой остров (среди группы небольших)
maritime climate - морской (приморский) климат
moor - торфянистая местность, торфяник; болото
plentiful - изобилующий, обильный; богатый
range – ряд, гряда (mountain range — гряда гор, горная цепь)
rolling lowland terrain - холмистая низинная местность
temperate - умеренный
unpredictable - непредсказуемый
World Heritage Site – Мировое культурное наследие (памятник)
Abbrevations
ft. – feet (foot)
m. - metres
km² - square kilometres
Plant and Animal Life
England shares with the rest of Britain a diminished spectrum of vegetation and living creatures.
Today only a small part of the English countryside is woodland. Broad-leaved (oak, beech, ash, birch, and elm) and conifer (pine, fir, spruce, and larch) trees dominate the landscapes of Kent, Surrey, East Sussex, West Sussex, Suffolk, and Hampshire. A substantial amount of England's forestland is privately owned.
Certain Mediterranean species of plants exist in the sheltered and almost subtropical valleys of the southwest, while tundra-like vegetation is found in parts of the moorland of the northeast. England has a profusion of summer wildflowers in its fields, lanes, and hedgerows. Cultivated gardens, which contain many species of trees, shrubs, and flowering plants from around the world, account for much of the varied vegetation of the country.
Mammal species such as the bear, wolf, and beaver were exterminated in historic times, but others such as the fallow deer, rabbit, and rat have been introduced.
The bird life is unusually varied, mainly because England lies along the route of bird migrations. About 100 different species are recorded annually.
Foxes in small numbers have colonized woods and heaths within a short distance of the centre of London. There are few kinds of reptiles and amphibians — about half a dozen species of each.
Freshwater fish are numerous; the char and allied species of the lakes of Cumbria probably represent an ancient group, related to the trout. The marine fishes are abundant in species and in absolute numbers.
The great diversity of shorelines produces habitats for numerous types of animals.
Vocabulary notes
abundant in – обильный, богатый, имеющийся в изобилии, изобилующий (in - чем-л.)
allied species - родственные виды
amphibian – амфибия; земноводный
ash - ясень
beech - бук, буковое дерево
birch - берёза
broad-leaved - широколистный
char - ручьевая форель, пеструшка
conifer - хвойное дерево
diminished - сокращенный; ослабленный; истощенный
elm - вяз, ильм
(to) exterminate - искоренять; истреблять, ликвидировать
fallow deer - лань
fir - пихта; ель (тж. некоторые другие виды хвойных деревьев)
habitat - родина, место распространения, ареал (животного, растения); естественная среда (natural habitat — естественная среда обитания)
heath – вереск
hedgerow - зеленое ограждение
larch - лиственница
living creatures – живые существа
mammal - млекопитающее
oak - дуб
pine - сосна
profusion - изобилие, богатство; избыток; обильность, чрезмерность
reptile - рептилия
shoreline - береговая линия
spectrum - спектр, диапазон (spectra – мн.ч.)
species - вид, разновидность
spruce – ель; хвойное дерево
trout - форель
vegetation - растительность
London
London is the capital city of England and the United Kingdom.
London is today one of the world's leading business, financial and cultural centres, and its influence in politics, education, entertainment, media, fashion and the arts all contribute to its status as one of the major global cities.
London is the most populous city within city limits in the European Union with an official population of 7.6 million and has a metropolitan area population of around 13 million people. Its population is very cosmopolitan (a wide range of peoples, cultures and religions, speaking over 300 different languages). London is an international transport hub (centre), with five international airports and a large port. It serves as the largest aviation hub in the world, and its main airport, the multi terminal Heathrow, carries more international passengers than any other airport in the world.
Inner London includes the original City of London and 13 of London's 33 boroughs; Greater London includes all 33 boroughs.
One area of London which does have a strict definition is the City of London (usually just called The City), the largest financial district and central business district (CBD) in Europe. The City has its own governance and boundaries, giving it a status as the only completely autonomous local authority in London.
The West End is London's main entertainment and shopping district, with locations such as Oxford Street, Leicester Square, Covent Garden and Piccadilly Circus acting as tourist magnets. The West London area is known for fashionable and expensive residential areas such as Notting Hill, Knightsbridge and Chelsea — where properties can sell for tens of millions of pounds.
The eastern side of London contains the East End and East London. The East End is the area closest to the original Port of London, known for its high immigrant population, as well as for being one of the poorest areas in London. North London and South London are informal divisions of the capital made by the River Thames.
London is a major tourist destination, with four world heritage sites and numerous iconic landmarks such as Houses of Parliament, Tower Bridge, the Tower of London, Westminster Abbey, Buckingham Palace and the London Eye amongst its many attractions, along with famous institutions such as the British Museum and the National Gallery, Madame Tussaud's Wax Museum and so on.
Exhibitions of wax figures are still popular, the most famous being those of Marie Tussaud in London. Her museum contains a variety of historical figures, including the original models she made of her great contemporaries, including Voltaire and Benjamin Franklin.
British Museum is a Britain's national museum of archaeology and antiquities, established in London in 1753 when the government purchased three large private collections consisting of books, manuscripts, prints, drawings, paintings, medals, coins, seals, cameos, and natural curiosities.
The British Library is now one of the world's largest and most comprehensive collections of books, drawings, Chinese ceramics and the natural-history collections.
Tate Gallery is an art museum housing the national collection of British painting and sculpture and of modern British and European art since 1870. It is named after Sir Henry Tate (1819-1899), a sugar refiner and inventor of the sugar cube, who donated his collection of Victorian art to the nation in 1890.
There are many famous historic landmarks in London. The Palace of Westminster, known also as the Houses of Parliament, is where the two Houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (the House of Lords and the House of Commons) conduct their sittings. The Palace lies on the north bank of the River Thames in the London borough of the City of Westminster.
Big Ben is one of the most famous landmarks in the world. The clock tower is situated on the banks of the River Thames and is part of the Palace of Westminster. Officially Big Ben is only the name of the biggest of the five bells in the clock tower also known as St Stephen's Tower.
Buckingham Palace is one of the most popular landmarks in London. It is the London home of the British Royal family. The 600 room palace is surrounded by a 40 acre garden.
Tower of London on the north banks of the River Thames, was built by William the Conqueror, following his successful invasion in 1066. It has been added to over the years by the various monarchs. The Tower, or Bloody Tower as it is known, has been host to many famous executions and imprisonments, including those of Anne Boleyn, Catherine Howard, Lady Jane Grey and Sir Walter Raleigh. The Jewel House, which houses the Crown Jewels, lies within the confines of the Tower of London.
The London Eye, next to County Hall, is another of London’s most modern landmarks. It is the world’s biggest ferries wheel, and will carry 800 passengers at a time on a thirty-minute ride. From its highest point of 450 feet, it promises views of up to 25 miles.
St Paul’s Cathedral is one of the most popular landmarks in London The dome of St Paul's Cathedral is the second biggest dome in the world, after St Peter's in Rome.
The Millennium Dome in London is the largest dome in the world, covering
over 180 acres; it is 320m in diameter and 50m high with support towers
reaching 100m. It was built on the Greenwich Meridian (0 degrees longitude) to commemorate the ringing in of the new millennium.
There are many monuments in London: The Monument in the City of London commemorating the Great Fire of London; Marble Arch and Wellington Arch, the Albert Memorial and Royal Albert Hall in Kensington; Nelson's Column is a nationally-recognised monument in Trafalgar Square.
Often called "The Green City" London has a number of parks. The largest of these are the Royal Parks of Hyde Park and its neighbours Kensington Gardens and Holland Park Gardens in the centre of London, Regent's Park on the northern edge, Royal Parks of Greenwich Park to the south east, and Bushy Park and Richmond Park to the south west of the city centre.
Vocabulary notes
antiquity - древность; старина; классическая древность, античность
borough - городок, небольшой город
(to) confine - заключать в тюрьму; заточать, держать взаперти
dome – купол
(to) donate - дарить, жаловать, жертвовать
execution - казнь; уничтожение, разрушение
ferris wheel - чертово колесо ( аттракцион )
hub - центр ( событий, внимания, деятельности )
landmark – достопримечательность
imprisonment - заключение
metropolitan area - столичная зона; большой Лондон (включающий все муниципальные районы)
Abbreviation
archit. - architecture
B.L. – British Library
bldg(s) – building(s)
boro. – borough
CBD - central business district
Lond. – London
Largest cities
The list of United Kingdom top cities by population:
1) London, with the population of 7,509,000 people;
2) Birmingham - 1,001,000 people;
3) Glasgow, - 629,501 people.
Other major cities with urban area populations in excess of 250,000 inhabitants are - alphabetically - Belfast, Bradford, Bristol, Cardiff, Coventry, Edinburgh, Kingston Upon Hull, Leeds, Leicester, Liverpool, Manchester, Nottingham, Sheffield, Stoke on Trent and Wolverhampton. The most prominent of them are the following ones:
Birmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands, England. Birmingham is the largest of England's core cities, and is considered to be the United Kingdom's second city. It includes several neighbouring towns and cities, such as Solihull, Wolverhampton and the towns of the Black Country. Birmingham is situated just to the west of the geographical centre of England on the Birmingham Plateau between the basins of the Rivers Severn and Trent. The city's reputation was forged as a powerhouse of the Industrial Revolution in Britain. It is a center of various industries such as the iron and steel industry.
Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland and third most populous in the United Kingdom. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's west central lowlands. From the 18th century the city had become a hub of transatlantic trade with the Americas. The city and surrounding region is one of the world's centres of heavy engineering and shipbuilding, constructing many famous vessels. Today it is one of Europe's top twenty financial centres and is home to many of Scotland's leading businesses.
Manchester is one of the largest industrial cities in the UK. The city centre is on the east bank of the River Irwell, near the confluence of the River Medlock and the River Irk and is relatively low-lying. The River Mersey flows through the south of Manchester. Manchester is often described as the “Capital of the North”. Manchester today is a centre of the arts, the media, higher education and commerce. It is the third most visited city in the United Kingdom by foreign visitors, after London and Edinburgh. Manchester is also well known for its sporting connections, with two major Premier League football teams, Manchester United and Manchester City. Manchester is credited as the world's first industrialised city. It is a centre of the textile region and a chief cotton manufacturing city.Manchester City Centre is now on of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, mainly due to its network of canals and mills.
Sheffield is the centre of heavy industry. It is often called the city of steel. It is situated in South Yorkshire, England. It is so named because of its origins in a field on the River Sheaf that runs through the city.
Edinburgh is the capital of Scotland and its second-largest city. It is in the south-east of Scotland, on the east coast of Scotland's "Central Belt", on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, on the North Sea and, because of its rugged setting and vast collection of Medieval and Georgian Architecture including numerous stone tenements, it is one of the most dramatic cities in Europe. The city was one of the major centres of the enlightenment, led by the University of Edinburgh. The Old Town and New Town districts of Edinburgh were listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995. Edinburgh is well-known for the annual Edinburgh Festival, a collection of official and independent festivals held annually over about four weeks from early August.
Liverpool is a city in North West England situated along the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary. Liverpool is one of England's core cities and it’s fifth most populous — 447,500. It is an industrial city (textile industry) and a principal port of Western England. Liverpool is internationally known as a cultural centre, with a particularly rich history in popular music (most notably The Beatles), performing and visual arts.
Cardiff is the capital, largest and core city of Wales. It was a major port for the transport of coal following the arrival of industry in the region. It serves as a major centre of culture, sport and history in the United Kingdom. Cardiff have the largest concentration of Castles of any city in Europe. It is situated to the south by the Bristol Channel. The River Taff winds through the centre of the city and together with the River Ely flows into the freshwater lake of Cardiff Bay. A third river, the Rhymney flows through the east of the city entering directly into the Bristol Channel. A fourth river, the Lleucu has been culverted.
Belfast is the capital of Northern Ireland. It is situated on Northern Ireland`s eastern coast. Belfast is also located at the eastern end of Belfast Lough and at the mouth of the River Lagan making it an ideal location for the shipbuilding industry that once made it famous (the Titanic was built in Belfast in 1912).
Bristol is one of the centres of culture, employment and education in the region. It served as the commercial port but now its economy is based on the aerospace industry, and the city centre docks have been regenerated as a centre of heritage and culture. Bristol is 15 miles (185 km) west of London and has a short coastline on the estuary of the River Severn which flows into the Bristol Channel.
Vocabulary notes
confluence - слияние ( рек ); пересечение ( дорог )
dramatic - волнующий, яркий
Enlightment – образование, обучение, просвещение; просвещенность (the age of Enlightenment — эпоха Просвещения)
estuary - дельта; устье реки
metropolitan borough - столичное городское поселение, столичный муниципальный район
populous - густонаселенный; (много)людный
rugged - пересеченный, заваленный, труднопроходимый (о местности) surrounding - ближайший, ближний, близлежащий, соседний, окружающий
tenement – владение; обитель
Abbreviations
UNESCO - United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (Организация ООН по вопросам образования, науки и культуры, ЮНЕСКО)
