Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку для подготовки студентов к интернет-тестированию Уфа 2007
| Вид материала | Учебно-методическое пособие |
СодержаниеCommon Abbreviations The united kingdom of great britain Political system |
- Учебно-методическое пособие Санкт-Петербург 2001 удк 681. 3 Бобцов А. А., Лямин, 1434.37kb.
- Название работы, 564.65kb.
- Учебное пособие Для подготовки к тестированию Новочеркасск 2007, 2155.67kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Криминалистика», 121.72kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Эконометрика», 503.64kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Психология и педагогика», 723.57kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Международное, 422.1kb.
- Методические указания по выполнению семестровой контрольной работы с комплектом заданий, 701.46kb.
- Учебное пособие по английскому языку для студентов экономистов. Автор-составитель Большакова, 15.76kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Финансы», 513kb.
Common Abbreviations
A.B. Artium Baccalaureus [Bachelor of Arts]
abbr. abbreviation(s), abbreviated
Acad. Academy
A.D. anno Domini [in the year of the Lord]
alt. altitude
A.M. ante meridiem [before noon]; Artium Magister [Master of Arts]
AM amplitude modulation
Assn. Association
at. no. atomic number
at. wt. atomic weight
Aug. August
Ave. Avenue
AWOL absent without leave
b. born, born in
B.A. Bachelor of Arts
B.C. Before Christ
b.p. boiling point
B.S. Bachelor of Science
Btu British thermal unit(s)
C Celsius (centigrade)
c. circa [about]
cal calorie(s)
Capt. Captain
cent. century, centuries
cm centimeter(s)
co. county
Col. Colonel; Colossians
Comdr. Commander
Corp. Corporation
Cpl. Corporal
cu cubic
d. died, died in
D.C. District of Columbia
Dec. December
dept. department
dist. district
div. division
Dr. doctor
E east, eastern
ed. edited, edition, editor(s)
est. established; estimated
et al. et alii [and others]
F Fahrenheit
Feb. February
fl. floruit [flourished]
fl oz fluid ounce(s)
FM frequency modulation
ft foot, feet
gal. gallon(s)
Gen. General, Genesis
GMT Greenwich mean time
GNP gross national product
GOP Grand Old Party (Republican Party)
Gov. governor
grad. graduated, graduated at
H hour(s)
Hon. the Honorable
hr hour(s)
i.e. id est [that is]
in. inch(es)
inc. incorporated
Inst. Institute, Institution
IRA Irish Republican Army
IRS Internal Revenue Service
Jan. January
Jr. Junior
K Kelvin
kg kilogram(s)
km kilometer(s)
£ libra [pound], librae [pounds]
lat. latitude
lb libra [pound], librae [pounds]
Lib. Library
long. longitude
Lt. Lieutenant
Ltd. Limited
m meter(s)
M minute(s)
M.D. Medicinae Doctor [Doctor of Medicine]
mg milligram(s)
mi mile(s)
min minute(s)
mm millimeter(s)
mph miles per hour
Mr. Mister (always abbreviated)
Mrs. Mistress (always abbreviated)
Msgr Monsignor
mt. Mount, Mountain
mts. mountains
Mus. Museum
N north; Newton(s)
NAACP National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
NASA National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organization
NE northeast
no. number
Nov. November
OAS Organization of American States
Oct. October
Op. Opus [work]
oz ounce(s)
pl. plural
pop. population
pseud. pseudonym
pt. part(s)
pt pint(s)
pub. published; publisher
qt quart(s)
Rev. Revelation; the Reverend
rev. revised
R.N. registered nurse
rpm revolution(s) per minute
RR railroad
S south
S second(s)
SEATO Southeast Asia Treaty Organization
SEC Securities and Exchange Commission
sec second(s); secant
Sept. September
Ser. Series
Sgt. Sergeant
sq square
Sr. Senior
St. Saint; Street
UNICEF United Nations Children's Fund
uninc. unincorporated
Univ. University
U.S. United States
USA United States Army
USAF United States Air Force
USCG United States Coast Guard
USMC United States Marine Corps
USN United States Navy
VFW Veterans of Foreign Wars
VISTA Volunteers in Service to America
vol. volume(s)
vs. versus
W west; watt(s)
WHO World Health Organization
wt. weight
yd yard(s)
YMCA Young Men's Christian Association
YWCA Young Women's Christian Association
TESTS
1. How many states are there in the United States?
1. 48 2. 50 3. 51 4. 52
2. What is the capital city of the USA?
1. New York 2. Los Angeles 3. Philadelphia 4. Washington, D.C.
3. What is the largest state?
1. Alaska 2. California 3. Hawaii 4. Rhode Island
4. What is the smallest state?
1. Texas 2. Alaska 3. Rhode Island 4. Ohio
5. What is the longest river?
1. Mississippi 2. Hudson 3. Colorado 4. Potomac River
6. What is the residence and office of the President of the USA?
1. The Capitol 2. The White House 3. Lincoln Memorial 4. Pentagon
7. Where does Congress (the Senate and the House of Representatives) meet ?
1. in the Capitol 2. the White house 3. Lincoln Memorial 4. Pentagon
8. The first capital of the USA was…
1. Washington D.C. 2. New York 3. Philadelphia 4. Olympia
9. What is the name of the river that runs through Washington, D.C.?
1. Colorado 2. Mississippi 3. Potomac River 4. Hudson
10. The Grand Canyon is in…
1. Nevada 2. Arizona 3. California 4. Colorado
11. The Golden Gate Bridge is in…
1. California 2. Oregon 3. Florida 4. Texas
12. The Disneyland Resort is in…
1. Los Angeles 2. San Francisco 3. Anaheim 4. Sacramento
13. Mount Rushmore in South Dacota is…
1. the highest mountain
2. the lowest mountain
3. a mountain with the faces of four presidents
4. a mountain with the face of the first president
14. Who was the first President of the USA ?
1. G. Washington 2. Thomas Jefferson 3. Benjamin Franklin 4. A. Lincoln
15. The Fourth of July is …
1. Memorial Day 2. St. Patrick’s Day 3. Independence Day 4. President’s Day
16. What was the main reason of Civil War (1861-1865) ?
1. slavery 2. independence from Britain 3. religion 4. new Constitution
17. The stock market crashed and began the Great Depression in…
1. 1776, July 4. 2. 1863 3. 1929, October 29 4. 1945, August 6
18. Who issued the Emancipation Proclamation, granting freedom to slaves in Confederate-held territory?
1. President Jefferson
2. President Truman
3. President Lincoln
4. President Washington
19. What is called “the Star Spangled Banner”?
1. the American Flag 2. the Coat of Arms 3. a political party 4. a famous monument
20. John Steinbeck was …
1. a musician 2. a scientist 3. a president 4. a writer
21. Who wrote “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” ?
1. Jack London
2. Benjamin Franklin
3. Harriet Beecher Stowe
4. Theodore Dreiser
22. SAMUEL CLEMENS was the real name of…
1. Theodore Dreiser 2. Mark Twain 3. Jack London 4. Ernest Hemingway
23. Babe Ruth was …
1. a baseball player 2. a basketball player 3. a football player 4. a soccer player
24. What is the official language of the USA?
1. English
2. there’s no current official language
3. English and Spanish
4. French
25. The biggest city in the USA is…
1. Chicago 2. New York 3. Los Angeles 4. Washington D.C.
THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN
AND NORTHERN IRELAND
National symbols
T


he flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag commonly known as the "Union Jack". Created from the superimposition of the flags of England (St George's Cross) and Scotland (Saint Andrew's Cross), with the Saint Patrick's cross, representing Ireland, being added to this in 1801.
Flag Coat of Arms
| Country | Patron saint | Flower (symbol) |
| England | St. George | Red rose |
| Scotland | St. Andrew | Cotton thistle |
| Wales | St. David | Leek/Daffodil |
| Northern Ireland | St. Patrick | Shamrock/Flax |
The national anthem of the United Kingdom is God Save the King, with "King" replaced with "Queen" whenever the Monarch is female. The anthem's name, however, remains God Save the King.
Britannia is a personification of the UK, originating from the Roman occupation of southern and central Great Britain. Britannia is symbolized as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag. Sometimes she is depicted as riding the back of a lion. At and since the height of the British Empire, Britannia has often associated with maritime dominance, as in the patriotic song Rule Britannia.
The lion has also been used as a symbol of the UK; one is depicted behind Britannia on the 50 pence piece and one is shown crowned on the back of the 10 pence piece. It is also used as a symbol on the non-ceremonial flag of the British Army. Lions have been used as heraldic devices many times, including in the royal arms of both the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Wales. The lion is featured on the emblem of the England national football team, giving rise to the popular football anthem Three Lions, and the England national cricket team.
The bulldog is sometimes used as a symbol of Great Britain, and is often associated with Winston Churchill's defiance of Nazi Germany.
The ancient British landscape, and especially some of its distinctive fauna such as the oak tree and the rose, have long been a widely used for the visual representation of British identity. The red rose is the emblem of the England national rugby union team.
Vocabulary notes
anthem– гимн
arms – герб
Corinthian helmet – коринфский шлем
daffodil - желтый нарцисс (национальная эмблема валлийцев)
defiance - вызов (на поединок, спор); пренебрежение; сопротивление, открытое неповиновение;
flax - лен (растение)
identity - индивидуальность; своеобразие; отличительная черта, особенность (national identity — национальные особенности)
leek - лук-порей (тж. и как национальная эмблема Уэльсa)
maritime - морской; приморский
patron saint - святой покровитель
personification - персонификация, олицетворение; воплощение
shamrock - трилистник (тж. эмблема Ирландии в виде трилистника)
shield - щит
superimposition– наложение, совмещение
thistle - чертополох (тж. как эмблема Шотландии)
prong - зубец ( вилки, вил и т. п. ); зуб
trident – трезубец
Abbreviations
GB and GBR - Great Britain
UK - the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
History
The early pre-Roman inhabitants of Britain were Celtic-speaking peoples, including the Brythonic people of Wales, the Picts of Scotland, and the Britons of Britain. Celts also settled in Ireland c. 500 BC.
Julius Caesar invaded and took control of the area 55-54 BC. The Roman province of Britannia endured until the 5th century and included present-day England and Wales.
In the 5th century Nordic tribes of Angles, Saxons, and Jutes invaded Britain.
Christianity began to flourish in the 6th century.
During the 8th-9th century, Vikings, particularly Danes, raided the coasts of Britain.
In the late 9th century Alfred the Great repelled a Danish invasion, which helped bring about the unification of England under Athelstan. The Scots attained dominance in Scotland, which was finally unified under Malcolm II (1005-34). William of Normandy (see William I the Conqueror) took England in 1066. The Norman kings established a strong central government and feudal state. The French language of the Norman rulers eventually merged with the Anglo-Saxon of the common people to form the English language.
From the 11th century, Scotland came under the influence of the English throne.
Henry II conquered Ireland in the late 12th century. His sons Richard I and John had conflicts with the clergy and nobles, and eventually John was forced to grant the nobles concessions in the Magna Carta (1215).
The concept of community of the realm developed during the 13th century, providing the foundation for parliamentary government. During the reign of Edward I, statute law developed to supplement English common law, and the first Parliament began to function.
In 1314 Robert Bruce (see Robert I) won independence for Scotland.
The Tudors became the ruling family of England following the Wars of the Roses (1455-85).
Henry VIII established the Church of England and incorporated Wales as part of England.
The reign of Elizabeth I began a period of colonial expansion; 1588 brought the defeat of the Spanish Armada.
In 1603 James VI of Scotland ascended to the English throne, becoming James I, and established a personal union of the two kingdoms. The English Civil Wars started in 1642 between Royalists and Parliamentarians, ending in the execution of Charles I (1649). After eleven years of Puritan rule under Oliver Cromwell and his son (1649-60), the monarchy was restored with Charles II.
The Great Plague (1664-66) broke out and up to 100,000 people died in London. This was the worst and the last of the epidemics. The disease spread throughout the country, but from 1667 only sporadic cases appeared until 1679. The plague's decline was attributed to various causes, including the Great Fire of London (September 2-5, 1666). Worst fire in London's history. It destroyed a large part of the city, including most of the civic buildings, St. Paul's Cathedral, 87 parish churches, and about 13,000 houses.
In 1707 England and Scotland assented to the Act of Union, forming the kingdom of Great Britain.
The Hanoverians ascended to the English throne in 1714, when George Louis, elector of Hanover, became George I of Great Britain. During the reign of George III, Great Britain's American colonies won independence (1783). This was followed by a period of war with revolutionary France and later with the empire of Napoleon (1789-1815).
In 1801 legislation united Great Britain with Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
Britain was the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century, and it remained the world's foremost economic power until the late 19th century.
During the reign of Queen Victoria, Britain's colonial expansion reached its zenith, though the older dominions, including Canada and Australia, were granted independence (1867 and 1901, respectively).
The United Kingdom entered World War I allied with France and Russia in 1914. Following the war, revolutionary disorder began in Ireland, and in 1921 the Irish Free State (see Ireland) was granted dominion status. The six counties of Ulster, however, remained in the United Kingdom as Northern Ireland.
The United Kingdom entered World War II in 1939. Following the war the Irish Free State became the Irish Republic and left the Commonwealth. India also gained independence from the United Kingdom.
Throughout the postwar period and into the 1970s, the United Kingdom continued to grant independence to its overseas colonies and dependencies.
With U.N. forces, it participated in the Korean War (1950-53). In 1956 it intervened militarily in Egypt during the Suez Crisis. In 1982 it defeated Argentina in the Falkland Islands War.
As a result of continuing social strife in Northern Ireland, it joined with Ireland in several peace initiatives, which eventually resulted in an agreement to establish an assembly in Northern Ireland. In 1997 referenda approved in Scotland and Wales devolved power to both countries, though both remained part of the United Kingdom.
Vocabulary notes
attain - добиваться, достигать
clergy – духовенство
conquer - завоевывать, покорять; порабощать; подчинять; подавлять (силой оружия)
(to) devolve - передавать (права, полномочия, обязанности и т. п.; кому-л. - on/upon); переходить к другому лицу (о должности, обязанностях, имуществе и т. п.)
dominion – доминион; владение;
expansion - увеличение, расширение; распространение, экспансия; рост, развитие
flourish - процветать, преуспевать, быть в расцвете (сил), быть на вершине (о людях, начинаниях)
(to) intervene - вмешиваться; вклиниваться, вступаться
(to) invade - вторгаться; захватывать, оккупировать
legislation - законодательство; законодательная деятельность; закон; законопроект
(the) Magna Carta - Великая хартия вольностей (1215)
(to) merge - поглощать; сливать(ся), соединять(ся) (with)
reign - правление, царствование
referendum - референдум, всенародный опрос (referenda- мн.ч.)
ruler - властелин, правитель
statute law - право, выраженное в законах; законы, статутное право, "писаный закон"; (common law - общее право; неписаный закон)
strife - борьба; раздор, спор, соперничество
tribe - племя
Abbrevations
A.-S. – Anglo-Saxons;
U.N. – United Nations;
Political system
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (usually shortened to the United Kingdom, the UK or Britain) is a constitutional monarchy composed of four constituent countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The United Kingdom is a Constitutional Monarchy, with executive power exercised on behalf of the monarch by the Prime Minister and other cabinet ministers. The monarch technically holds all executive power and must nominate a head of government (Prime Minister) that the Parliament agrees upon. The Prime Minister is a member of the House of Commons.
The cabinet, including the Prime Minister, and other senior ministers collectively make up Her Majesty's Government. These ministers are drawn from, and are responsible to, Parliament.
T

he Prime Minister appoints ministers to government posts, usually from senior members of their own party. Most ministers are members of the House of Commons. The remaining ministers are usually from the House of Lords, Ministers do not legally have to come from Parliament.
The Palace of Westminster, on the banks of the River Thames, London, houses the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
Parliament is composed of the elected House of Commons and the unelected House of Lords. The House of Commons is the more powerful of the two houses. The members of the House of Commons are directly elected from single-member constituencies based on population. The House of Lords is constituted of life peers, hereditary peers, and bishops of the Church of England. (The House of Lords Act 1999 removed the automatic inheritance of seats in the Lords and permitted 92 hereditary peers to remain.) The Church of England is the established church of the state in England only.
The Scottish Parliament, National Assembly of Wales and Northern Ireland Assembly each have their own executives and separate law making and constitutional powers. In the United Kingdom, the monarch has extensive theoretical powers, but his/her role is mainly, though not exclusively, ceremonial. The monarch is an integral part of Parliament and theoretically gives Parliament the power to meet and create legislation. An Act of Parliament does not become law until it has been signed by the monarch (known as Royal Assent), although not one has refused assent to a bill that has been approved by Parliament since Queen Anne in 1708. The present monarch is Queen Elizabeth II who acceded to the throne in 1952 and was crowned in 1953.
The monarch is also Head of State of fifteen other Commonwealth Realms, including Canada, Australia, New Zealand and Jamaica. The Crown Dependencies
of the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man, formally possessions of the Crown, form a federacy with the United Kingdom collectively known as the British Islands. The UK also has fourteen overseas territories, all remnants of the British Empire (a quarter of the world's surface and population).
The Commonwealth of Nations (CN), usually known as the Commonwealth and formerly as the British Commonwealth, is a voluntary association of 53 independent sovereign states all of which are former possessions of the British Empire, except for Mozambique and the United Kingdom itself.
Queen Elizabeth II is the Head of the Commonwealth, In practice, the Queen heads the Commonwealth in a symbolic capacity, and it is the Commonwealth Secretary-General who is the chief executive of the organisation.
Elizabeth II is also the Head of State, separately, of sixteen members of the Commonwealth, called Commonwealth Realms. And each Realm is an independent kingdom. Beyond the Realms, the majority of the members of the Commonwealth have their own, separate Heads of State: thirty-one members are Commonwealth republics and five members have their own monarchs (Brunei, Lesotho, Malaysia, Swaziland, and Tonga).
The Commonwealth is primarily an organization in which countries with diverse economic backgrounds have an opportunity for close and equal interaction. The primary activities of the Commonwealth are designed to create an atmosphere of economic co-operation between member nations, as well as the promotion of democracy, human rights, and good governance in those nations.
The Commonwealth is not a political union, and does not allow the United Kingdom to exercise any power over the affairs of the organisation's other members.
E

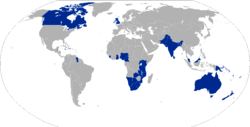
very four years the Commonwealth's members celebrate the
The flag of the CN The Commonwealth of Nations as of 2006
Commonwealth Games, the world's second-largest multi-sport event after the Olympic Games.
The United Kingdom is one of the three countries in the world today that does not have a codified constitution (the other two being New Zealand and Israel), relying instead on traditional customs and separate pieces of constitutional law.
At present there are two main political parties in England. The Conservative (or Tory) Party started as Royalists in the 17th century. Now it represents the interests of the big landowners, the bankers and the industrialists. The Labour Party was established at the beginning of this century. It was set up by the trade-unions and various small socialist groups. But now there isn’t much difference between the two parties.
Tony Blair was elected in 1997. The current Prime Minister is Gordon Brown.
Vocabulary notes
Assent – согласие; одобрение, утверждение, разрешение, санкция (Royal assent — королевская санкция (одобрение монархом законопроекта))
Bishop - епископ (Anglican bishop — епископ протестантской церкви)
Chief executive - глава исполнительной власти; губернатор штата; зд. глава правительства
Codify - составлять кодекс, кодифицировать
Commonwealth of Nations - Содружество Наций
Dependency - зависимая страна, зависимая территория
Executive power – исполнительная власть
Hereditary peer - наследственный пэр
Life peer - пожизненный пэр (лицо, получившее титул барона), дающий право быть членом палаты лордов [House of Lord], но не передающийся по наследству;
Realm - государство, королевство
Abbrevations
CN - the Commonwealth of Nations
H.C. – House of Commons
H.L. - House of Lords
MP – member of parliament
PM – prime minister
