Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку для подготовки студентов к интернет-тестированию Уфа 2007
| Вид материала | Учебно-методическое пособие |
- Учебно-методическое пособие Санкт-Петербург 2001 удк 681. 3 Бобцов А. А., Лямин, 1434.37kb.
- Название работы, 564.65kb.
- Учебное пособие Для подготовки к тестированию Новочеркасск 2007, 2155.67kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Криминалистика», 121.72kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Эконометрика», 503.64kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Психология и педагогика», 723.57kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Международное, 422.1kb.
- Методические указания по выполнению семестровой контрольной работы с комплектом заданий, 701.46kb.
- Учебное пособие по английскому языку для студентов экономистов. Автор-составитель Большакова, 15.76kb.
- Учебно-методическое пособие для подготовки к тестированию по курсу: «Финансы», 513kb.
Министерство образования и науки Российской Федерации
Федеральное агентство по образованию
Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессиального
образования
«УФИМСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ НЕФТЯНОЙ
ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
Кафедра иностранных языков
УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКОЕ ПОСОБИЕ
по английскому языку для подготовки студентов к интернет-тестированию
Уфа 2007
ENGLISH-SPEAKING COUNTRIES
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
General information
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states, one federal district, and fourteen territories. The country is situated almost entirely in the western hemisphere. The U.S. is one of the world's most ethnically and socially diverse nations, the product of large-scale immigration from almost every corner of the globe. Its national economy is the world's largest, with a nominal 2005 gross domestic product (GDP) of more than $13 trillion.
The nation was founded by thirteen colonies of Great Britain located along the Atlantic seaboard.
Etymology
Common abbreviations of the United States of America include the United States, the U.S., and the U.S.A. Colloquial names for the country include the common America as well as the States. The term Americas, for the lands of the western hemisphere, was coined in the early sixteenth century after Amerigo Vespucci, an Italian explorer and cartographer. The full name of the country was first used officially in the Declaration of Independence, which was the "unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America" adopted by the "Representatives of the united States of America" on July 4, 1776. The current name was finalized on November 15, 1777, when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation, the first of which states, "The Stile of this Confederacy shall be 'The United States of America.'" Columbia, a once popular name for the Americas and the U.S., was named after Christopher Columbus. It appears in the name District of Columbia.
Symbols
The American Flag
|
|
|
|
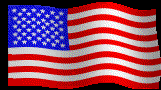
The American flag consists of 13 horizontal stripes, 7 red alternating with 6 white. The upper corner near the staff is a rectangular blue field that contains 50 five-pointed white stars. The thirteen stripes symbolize the 13 original colonies of the United states of America and the stars represent the 50 states of the Union.
White is said to symbolize purity and innocence; Red, hardiness and valor, and Blue, vigilance, perseverance and justice. The American flag is commonly called the Stars and Stripes, the Red, White and Blue, or the Star Spangled Banner.
History of American Flag
For more than 200 years, the American flag has been the symbol of the nation's strength and unity.
On June 14, 1777, in order to establish an official flag for the new nation, the Continental Congress passed the first Flag Act: "Resolved, That the flag of the United States be made of thirteen stripes, alternate red and white; that the union be thirteen stars, white in a blue field, representing a new Constellation." As new states joined the Union there had to be representation of them in the flag.
Betsy Ross
Elizabeth Griscom Ross was a seamstress and legend has said that she was the maker of the first American flag. According to the story often told, General George Washington, her late husband’s uncle, called her in 1773 and asked her to design a national flag. The Betsy Ross house has been preserved and can be visited by tourists. It is located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Between 1777 and 1960, Congress passed several acts that changed the shape, design and arrangement of the flag and allowed for additional stars and stripes to be added to reflect the admission of each new state.
The coat of arms of the United States

Located at the west end of the Great Hall, closest to the Capitol, is the coat of arms of the United States. It was approved on 20 June 1782 by an Act of Congress, and appears on the Great Seal of the United States. Above the head of an American bald eagle is the crest, which represents a cloud surrounding thirteen stars. The eagle holds thirteen arrows of war in its left talon and the olive branch of peace in its right. In its beak is a scroll bearing the motto “e pluribus unum (out of many, one)”. The shield has thirteen vertical stripes (pales) on the lower portion, alternating white and red, with a wider horizontal bar (a chief) above, in blue.
The colors on the coat of arms are the same as those of the flag and when displayed have special meaning. Red represents hardiness and valor, the white purity and innocence, and the blue stands for vigilance, perseverance, and justice. The arrows and olive branch represent the power of peace and war, exclusively vested in Congress. The shield on the breast of the American eagle has no supporters (a pair of figures standing one on each side of and supporting the shield), denoting that the United States must rely on its own virtue. The thirteen bars of the shield represent the "several States all joined in one compact entire" and the solid horizontal bar (chief) above "unites the whole and represents Congress."
the Great Seal of the United States

On July 4, 1776, the Continental Congress passed a resolution authorizing a committee to devise a seal for the United States of America. This mission, designed to reflect the the Founding Fathers' beliefs, values, and sovereignty of the new Nation, became a reality on June 20, 1782.
The front side of the Great Seal, which is the U.S. coat of arms, authenticates the President's signature on numerous official documents such as treaty ratifications, international agreements, appointments of Ambassadors and civil officers, and communications from the President to heads of foreign governments. It is also shown on coins, postage stamps, passports, monuments and flags, and in many other ways. The American public sees both the front and less familiar reverse, which is never used as a seal, every day when using a $1 dollar bill.
On the front side, the American bald eagle is prominently featured supporting a shield composed of 13 red and white stripes representing the Thirteen Original States with a blue bar uniting the shield and representing Congress. The motto of the United States, E Pluribus Unum (meaning out of many, one), refers to this union. The olive branch and 13 arrows grasped by the eagle allude to peace and war, powers solely vested in the Congress, and the constellation of stars symbolizes the new Nation taking its place among the sovereign powers.
On the reverse side, the pyramid signifies strength and determination: The eye over it and the motto, “Annuit Coeptis (meaning He, [God,] has favored our undertakings)” allude to the many interventions of Providence in favor of the American cause. The Roman numerals below are the date of the Declaration of Independence. The words under it, “Novus Ordo Seclorum (meaning a new order of the ages)”, signify the beginning of the new American era in 1776.
Anthem of the United States.
The Star Spangled Banner
Lyrics
Oh, say can you see by the dawn's early light
What so proudly we hailed at the twilight's last gleaming?
Whose broad stripes and bright stars thru the perilous fight,
O'er the ramparts we watched were so gallantly streaming?
And the rocket's red glare, the bombs bursting in air,
Gave proof thru the night that our flag was still there.
Oh, say does that star-spangled banner yet wave
O'er the land of the free and the home of the brave?
On the shore, dimly seen through the mists of the deep,
Where the foe's haughty host in dread silence reposes,
What is that which the breeze, o'er the towering steep,
As it fitfully blows, half conceals, half discloses?
Now it catches the gleam of the morning's first beam,
In full glory reflected now shines in the stream:
'Tis the star-spangled banner! Oh long may it wave
O'er the land of the free and the home of the brave.
And where is that band who so vauntingly swore
That the havoc of war and the battle's confusion,
A home and a country should leave us no more!
Their blood has washed out of of their foul footsteps' pollution.
No refuge could save the hireling and slave'
From the terror of flight and the gloom of the grave:
And the star-spangled banner in triumph doth wave
O'er the land of the free and the home of the brave.
Oh! thus be it ever, when freemen shall stand
Between their loved home and the war's desolation!
Blest with victory and peace, may the heav'n rescued land
Praise the Power that hath made and preserved us a nation.
Then conquer we must, when our cause it is just,
And this be our motto: "In God is our trust."
And the star-spangled banner in triumph shall wave
O'er the land of the free and the home of the brave.
Anthem History
The text was written by the American lawyer and poet Francis Scott Key (1779-1843). During the night of September 13, 1814, the British fleet bombarded
Fort McHenry in the harbour at Baltimore, Maryland. Francis Scott Key, a 34-year old lawyer-poet, watched the attack from a deck of a British prisoner-exchange ship. As the battle ceased on the following morning, Key turned his telescope to the fort and saw the American flag was still waving. The sight so inspired him that he pulled a letter from his pocket and began to write the poem which eventually was adopted as the national anthem of the United States - "The Star Spangled Banner."
The melody to which Francis Scott Key intended his poem to be sung was the tune known as "to Anachreon in Heaven".The composer of this tune is uncertain. John Stafford Smith (1750-1836), used the tune for an arrangement and is often regarded as the composer of the tune.
Vocabulary notes
Contiguous – соприкасающийся, прилегающий
Gross domestic product – Валовый национальный продукт
Abbreviations - сокращения
Hemisphere - полушарие
Unanimous - единогласный
Purity - чистота
Innocence - невинность
Hardiness - смелость, отвага
Valor - доблесть
Vigilance - бдительность
Perseverance – упорство, настойчивость
Highlights -
Seamstress - швея
coat of arms – герб
crest - гребень
virtue - добродетель
authenticate – заверять, подтверждать
treaty – соглашение, конвенция
Ambassador - консул
Anthem - гимн
History
DISCOVERY
Around the year 1000 a party of Icelandic Vikings under Leif Ericson sailed to the eastern coast of North America. They landed at a place they called Vinland. Remains of a Viking settlement have been found in the Canadian province of Newfoundland. They failed, however, to establish any permanent settlements, and they soon lost contact with the new continent.
Five hundred years later, the need for increased trade and an error in navigation led to another European encounter with America. In late 15th-century Europe, there was a great demand for spices, textiles and dyes from Asia. Christopher Columbus, a mariner from Italy, mistakenly believed that he could reach the Far East by sailing 4,000 miles (6,400 kilometers) west from Europe. In 1492, he persuaded the king and queen of Spain to finance such a voyage. Columbus sailed west, but he did not reach Asia. Instead he landed on one of the Bahama Islands in the Caribbean Sea.
The Spanish established some of the earliest settlements in North America—St. Augustine in Florida (1565). Santa Fe in New Mexico (1609) and San Diego in California (1769).
The Europeans were initially drawn to the New World in search of wealth. When Columbus and later Spanish explorers returned to Europe with stories of abundant gold in the Americas, each European sovereign hastened to claim as much territory as possible in the New World— along with whatever wealth might be extracted from it. This was the main reason for the establishment of colonies.




