Сборник статей ежегодной международной студенческой научно-практической конференции isbn 978-5-7890-0605-4 Ростов-на-Дону
| Вид материала | Сборник статей |
- Сборник статей по материалам Международной научно-практической конференции по страхованию, 1875.83kb.
- Международной научно-практической конференции, 481.91kb.
- Программа XXIV студенческой научно-теоретической конференции 18-23 апреля 2011 г. Ростов-на-Дону,, 1754.34kb.
- Итоги и перспективы энциклопедических исследований сборник статей итоговой научно-практической, 3612.81kb.
- Д. С. Лихачёва и проблемы современного мегаполиса Сборник докладов участников международной, 3272.71kb.
- Сборник научных статей по материалам 2-й международной научно-практической Интернет-конференции, 2229.35kb.
- Ственный институт наука и студенты: новые идеи и решения Сборник материалов viii-й, 5467.94kb.
- Итоги и перспективы энциклопедических исследований сборник статей итоговой научно-практической, 3301.6kb.
- Программа 4-й Международной студенческой научно-технической конференции Конференция, 803.12kb.
- Сборник научных статей и докладов участников Поволжской научно-практической конференции, 4109.46kb.
Literature
- Нелегальная миграция мексиканцев в США: до и после НАФТА// potok.archipelag.ru/text/a041.php
- Карелина Н. А. Нелегальная миграция в США: до и после НАФТА // Нелегальная иммиграция. — Главный редактор В. А. Ионцев. Москва: МАКС Пресс, 2002, с. 94-105.
- Население США и России: что показала перепись// ссылка скрыта
- Википедия // ссылка скрыта
- Иммиграционная политика и использование иностранной рабочей силы в США // rsonal.ru/facts_about_countries/ssha/ssha_zakonodatel_stvo_v_oblasti_migracionnoj_politiki/
- Миграция в США: "нелегалы" вытесняют "туземцев" // co.uk/hi/russian/business/newsid_7629000/7629820.stm
Наливайченко Дмитрий
Don State Technical University
SPAM AND PROTECTION AGAINST IT
The article deals with the history of appearing SPAM (a mass dispatch of advertising and other information to the people who don't have a wish to receive it), types of SPAM and also preventive methods of struggle and economic sense of it.
Key words: SPAM, mass dispatch, the Internet users, advertising, swindlers, information, “Nigerian letters”, “Fishing”, message, letters, computer viruses, Can-spam Act.
Originally the word «SPAM» appeared in 1936. It was deciphered as SPiced hAM (a hot ham) and was a trade mark for Hormel Foods Company producing tinned meat. An advertising term SPAM became great popular due to the well-known sketch from show «Flying circus of Monty Payton» (1969) .The plot of the sketch was that all dishes in a cafe menu contained «SPAM», some even several times. When the character of the sketch who had come to this cafe with his wife, asked to bring him a dish without «SPAM» a waitress offered him a dish with «small amount of SPAM». The visitor was indignant and the chorus of the Vikings sitting at the next little tables started to sing a laudatory song about «SPAM». Then the sketch plunged into the chaos. In the end of the sketch the wife exclaimed: I do not love «SPAM»! In total this word was mentioned in the sketch more than hundred times.
Here is another version of appearing «SPAM». After the Second World War there were huge reserves of the tinned food which the American soldiers were supplied with. To sell the stale production, Hormel Foods Company organized an advertising campaign. The word «SPAM» was evident everywhere from show-windows of all cheap shops. It was written on boards of buses and trams. This word could be read on the facades of houses and in newspapers. Advertising of tinned food «SPAM» was continuously broadcast on radio. In fact, there was no possibility to get rid of this ad- it "rushed" to people’s eyes and sounded in all receivers.
But what’s «SPAM» nowadays? «SPAM» is a mass dispatch of commercial, political and other advertising messages to people who don’t have a wish to receive them.
There are different kinds of «SPAM». First of all «SPAM» means ads. Some companies which are engaged in the legal business advertise the goods or services by using «SPAM». They can make its dispatch independently but often they order it from companies (or from persons) which are specialized in it. Attractiveness of such advertising means rather low costs and, presumably, big coverage of potential customers.
Sometimes «SPAM» is used to entice money from the letter’s receiver. The most widespread way received the name «Nigerian letters» because the great quantity of such letters came from Nigeria. Such letters contain the message that the addressee of the letter can somehow receive a great sum of money, and the sender can help him or her with it. Then the sender of the letter asks to transfer a little money with require of official registration or an account opening. This sum also is the purpose of swindlers.
«FISHING» is one more way of swindle by means of «SPAM». It represents an attempt of spammers to entice number of a credit card or an access password to a system of on-line payment from the receiver of the letter. Such letter usually looks like a communique from bank administration. It says that the addressee should confirm data about himself; otherwise his account will be blocked. Also there is a website address (belonging to spammers) with the form which it is necessary to fill in. Among the data which is required to be informed, there are also ones which are necessary to swindlers. That the victim hasn’t guessed a deceit, registration on this website simulates registration of an official website of the bank.
Other kinds of «SPAM» are:
* Chain letters
* Political propaganda distribution
* Mass dispatch for a conclusion of post system out of operation (DoS-attack).
* Mass dispatch on behalf of other person to cause to him or her negative altitude.
* Mass dispatch of the letters containing computer viruses (for their initial distribution).
* Dispatch of the letters containing a sentimental story
Categories of «SPAM»:
Products 25 %
Finance 20 %
For adults 19 %
Deceit and fraud 9 %
Health 7 %
The Internet 7 %
Entertainment 6 %
Spiritual 4 %
Others 3 %
Some spammers use the well-known vulnerabilities in the software or computer viruses in order to take control of a great number computers connected with the Internet, and to use them for a spam sending.
It is obvious that «SPAM» brings an economic benefits to its senders. This means that users, despite the dislike of «SPAM», yet enjoy services advertised via «SPAM». As long as the returns exceed costs to overcome protection from «SPAM» it will not disappear. Thus, the most reliable way of struggle is refusal of the services advertised by means of a spam. There are proposals of the use of public condemnation, even giving up connection with people who buy goods and services advertised by «SPAM».
Nowadays «SPAM» becomes harmful because of the spam sending is even more often coming with virus attacks and illegal intrusion into information systems of the Internet users. For this reason the attention of the public, state structures of law-enforcement and legal agencies is drawn to «SPAM» problem abroad, and also in our country.
Since 1 January 2004 in the USA operates the federal law which received name Can-Spam Act. There are a lot of attempts to bring spammers to court, and sometimes such attempts are successful.
Никитина Любовь Ивановна
Don State Technical University
L’ECONOMIE FRANÇAISE APRES LA CRISE
The article describes the main causes of the world crisis and the consequences of the crisis for France. The resources which will help to overcome the crisis and the measures which were undertaken in order to overcome its effects upon the economy.
Key words : GDP (gross domestic product), unemployment, recession, debts, development, research, credit, transport infrastructure, high education , competitiveness.
La crise financière et économique que connaît la planète depuis 2007 marque la fin de l'ordre mondial établi après 1945 d’après Franck Biancheri consiste actuellement à la décomposition accélérée du " pilier occidental ", avec les États-Unis au cœur.
Après la crise l'Anglo-américain ne serait plus nécessairement synonyme de modernité et le Dollar ne serait plus roi.[2]
La crise des subprimes éclats pendant l’été 2007. Que sont des subprimes ?
Ce sont des crédits immobiliers garantis par la valeur des biens achetés.
accordés à des ménages américaines modestes, avec des taux variables et sur une longue période. Les subprimes ont été inserées parmi d’autres pour composer des produits financiers complexes. Au cours de l’année 2008, le monde de la finance est ébranlé par une série de faillites effectives, oiu évitées grâce àune intervation massive des Etats. Le monde de la finance prend alors conscience de la gravité de la crise , car beaucoup d’institutions financières ont investi dans ces produits financiers complexes et dans leurs dérivés. Comme les banques redoutent le défaut de paiement, elles cessent de prêter entre elles leurs liquidités , asséchant le marché interbancaire de la monnaie centrale.Les acteurs de l’économie réelle se retrouve privé de crédits pour financer leurs investissements et les entreprises des prêts à court terme[1].La crise provoque une augmentation rapide et significative du chômage.
L’économie française après la crise
Par rapport a la plupart des autres pays européens, La France a relativement bien encaissé le choc de la crise à court terme, tout du moins sur le plan de la production intérieure brute (PIB). En 2009, le recul du PIB en volume (-2,5%) y a ainsi été moindre qu’en Allemagne, au Royaume-Uni et en Italie (environ -5%), ainsi que dans l’ensemble de la zone euro (-4%).
Les facteurs qui ont permis d’atténuer le choc de la crise sont les mêmes qui tendent à limiter la vigueur de la reprise depuis lors.
l'Insee a publié les premiers résultats de l'activité économique au 4e trimestre 2010 [1]. Ils étaient plutôt décevants : le produit intérieur brut (PIB) n'a progressé que de 0,3 % par rapport au
trimestre précédent, confirmant le ralentissement engagé. Mais ces résultats permettent aussi de mesurer les principaux moteurs de l'économie française après deux ans de crise.
Au niveau du PIB, c'est-а-dire de l'ensemble des richesses produites par l'économie française, le niveau d'avant crise n'est toujours pas rattrapé: il manque encore 1,6 point par rapport à la mi-2008. Ce n'est pas la faute cependant de la consommation des ménages : fin 2010, elle était supérieure de deux points à son niveau d'avant la crise. En revanche, l'investissement des entreprises reste encore très faible, avec 9,5 points de retard sur 2008, même s'il a commencé à se redresser un peu. Et la situation est encore pire pour l'investissement des ménages (dans
l'immobilier) qui accuse toujours un déficit de 13 points par rapport à son niveau d'avant crise. Facteur aggravant : l'investissement public, qui avait déjà légèrement fléchi malgré le plan de relance, est de nouveau orienté à la baisse du fait de l'austérité à laquelle sont soumises les
collectivités locales. Enfin, le commerce extérieur se redresse rapidement tant au niveau des importations que des exportations. Toutefois, lui non plus n'a pas encore rattrapé son niveau d'avant la crise.[5 ]
La faiblesse de structurelle du tissu de petites et moyennes entreprises est préoccupante pour l’économie en France.En témoignant notamment les problèmes chroniques de rentabilité auxquels de très nombreuses entreprises font face , rencontrant souvent une situation financière difficile.
La France a les pertes de parts de marché àl’exportation d’année en année. Son appareil productif et commercial souffre de la concurrence accrue non seulement de l’Allemagne, mais de plusieurs autres pays d’Europe. Le niveau de la production potentielle devrait à terme subir une perte permanante , d’environ 3, 5% par rapport aux niveaux qui auraient prévalu sans la crise. Cela va conduire les entrprises à ajuster massivement et durablement leurs invesstissement et leurs effectifs employés. Pendant la crise plus de 490 000 emplois ont été perdus en deux années.Le taux de chômage relativement stable en 2010 (autour de 9, 5%).
L’économie française dispose encore de nombreux atouts :
-les ménages y sont faiblement endettés et leur taux d’épargne est relativement élevé.
-les grandes entreprises françaises réalisent dans l’ensemble de bonnes performances economiques et financieres , avec des leaders mondiaux dans des nombreux secteurs
( aéronatique/défense, construction, ingénierie, énergie, traitement de l’eau et des déchets, agro-alimentaire, grande distribution, assurance, tourisme , publicité, industrie de luxe, de la culture et des loisirs) ;
-le marché de l’immobilier résidentiel y est consideré comme sain, comme en témoigne notamment une absence de surcapacité globale ;
-en matière de service , la France constitue le 4 em plus gros exportateur mondial (derrière les Etats –Unis, le Royaume-Uni et Allemagne) et degage des excédents commerciaux;
-dans l’ensemble , les banques sont considérées comme plus solides en france que dans la plupart des pays d’Europe.
-compte tenu de la natalité et des flux migratoires, les perspectives démographiques en France sont parmi les plus favorables à la croissance que l’on trouve en Europe.
Pour élargir la perspective, il est intéressant de mentionner les classements internationaux qui utilisent une batterie de critères mesurant le degré de compétitivité ou d’atracrtivité. A titrre d’exemple, La France était située au 15 èm rang mondial dans le dernier palmères annuel de compétitivité qu’a établi le World économique Forum, à partir de plus de 110 facteurs et en comparant au total 139 pays.
Pour les entreprises transnationales, la France présente ainsi des avantages de localisation particulièrement favorables dans les domaines tels que le traitement fiscal des activités de recherche et développement (R&D), les prix de l’électricité, le pourcentage des 25-34 ans ayant un niveau de l’éducation supérieure, le taux de pénétration de l’Internet à haut débit.
D’après le rapport préparé par Joseph Stiglitz et Amartia Sen, le gouvernement français ne doit pas mesurer la richesse nationale que par le PIB et d’intégrer des indicateurs complémentaires (patrimoine, offre de services publics, niveau et répartition des revenus) et de mettre moins l’accent sur la mesure statistique de la production économique que sur celle du bien -être.(8)
Les pouvoirs publics se sont engagés dans une trajectoire prolongée de consolidation budgétaire et fiscale mais ils s’efforcent en même temps de préparer l’avenir en préservant –voire en renforçant –certains domaines cruciaux tels que l’enseignement supérieur et la R&D.
Les perspectives de la France sont sensiblement plus favorables si l’on raisonne sur la base d’un grand nombre d’indicateurs-au delà des seuls chiffres du PIB ou des exportations, surtout dans ce contexte de la sortie de la crise.
A long terme, différents facteurs devraient permettre à la France d’améliorer sa compétitivité, notamment la vigueur de son secteur tertiaire, une croissance démographique positive et certains avantages du site économique, tels que des infrastructures bien développées.
La littérature à consulter
1. Affilé B., Gentil C., Rimbert F..Les grands questions de l’économie contemporaine [Text]./France :letudiant.fr]-2010, 167p.
2. Crise mondiale - En route pour le monde d'après: La France, l'Europe et le monde dans la décennie 2010-2020'[Text], Franck Biancheri
3. Cabannes P.-Y et al., Quelle croissance de moyen terme après la crise ?, in :INSEE (dir.), L’économie française –comptes et dossiers –Insee Références- édition 2010, p.43-70
4. Dhont-Petrault E. et Mantout S., France Atrractiveness Scoreboard –Agence Française pour les invesstissement internationaux (AFII) et Centre d’analyse stratégique (CAS), Paris 2010.
5. Guillaume Duval Alternatives Economiques n° 300 - mars 2011
6. International Monetary Fund, France: Article IV Consultation- Staff Report, Washington, DC, IMF Country Report n 10/240, juillet 2010.
7. Lallement Rémi L’économie française après la crise : un cap difficile, mais possible à franchir.
DGAPanalyse Frankreich 10, Dezember 2010.
8. Stiglitz J. , Sen A. et Fitoussi J.-P., Report by the Commission on the Measurement of Economic Performance and Social Progress, Paris 2009.
9. World economic Forum. The Global Competitiveness Report 2010-2011, Genève 2010.
Никитина Любовь Ивановна
Don State Technical University, Russia
OFFSHORE TERRITORIES: PROS AND CONS
This article describes the offshore territories, including typical indicators of offshore companies, purposes of creating offshore territory, the positive and negative effects, and their impact on national economies in a whole.
Key words: Offshore territories, development, registration, taxes, limited liability, foreign investment, economy, employment, accumulation, equity market.
Offshore business stills remains an under-researched phenomenon in the system of international economic relations. The scientists attitude towards it is ambiguous and controversial. Therefore, the trends in its rapid development require a more detailed study. This necessity arises from the fact that the existence of offshore centers is an important factor in attracting foreign investment, in performing economic reforms and modernization of the management mechanism.
The aim of the report is to provide data on offshore areas, assessing to investigate their advantages and disadvantages, to study the state and trends in the development of the offshore business.
History of establishment;
Offshore territories appeared several thousand years ago. Originally they were the Commerce pirate cities of Phoenicia and Crete that had long controlled and frightened the Mediterranean people. Offshore business even at that time was profitable, but remained quite risky. A good example was made by the experience of Athens. After the authorities had imposed a two percent import and export tax from Greece the other countries began to go pass around Athens to avoid paying taxes. Later on small island states which did not impose taxes on traders began to appear. Traders preferred to sell goods not in their own countries (for example, in England) but transported them to islands where they were exempted from taxes. Despite the centuries-old activities of traders, the term “offshore” in the modern meaning was appeared only in the late 1950’s in the U.S., after some company managed to avoid state control of its activities by the principle of geographical selectivity, namely by changing the country of registration: the company took its activities out of the legal reach of the U.S. government.
There are typical indicators of offshore companies:
1) Offshore companies may be engaged in any activity (except certain types of activities, which require licensing procedures);
2) Limited liability: the owners are responsible for the obligations of the company only in the paid-up authorized capital for non-banking companies there are usually no restrictions on the minimum paid-up authorized capital;
3) in the country of registration the company must have a registered (legal) address and the agent, who may be a person, individuals or legal, whose duty is to actually be at the registered office and be the link between the state authorities of the country of registration and the company , and to maintain a real is not necessary;
4) the company has the right, to open up bank accounts in the world without any restriction, and if in the country of registration there no taxes, and obligatory audits are not, it is not demanded to inform the authorities about accounts in the country of registration are also acceptable;
5) The owners are determined by shares (registered or bearer), and in their turn they elect directors, and they already take all current solutions, such as opening accounts in a bank, borrowing or lending, and etc.; directors appoint the company a secretary of the company, whose signature certifies the reports of all assemblies and decisions of the board of directors and shareholders;
6) The owners may be any legal parties or individuals;
7) The most important criterion: the company must operate it’s activity only outside the country of registration and not have any source of income its territory, including having no deals with local legal parties or individuals.
Purposes of creating offshore territory:
- Economic:
- foreign investment
- increase of foreign exchange earnings to the economy of the country
- Social:
- development acceleration of the country
- increasing employment and the population income
- Scientific and technical:
- leading foreign technologies launching in the field of modern telecommunications and banking
Such goals may vary depending on the particular situation and the type of an offshore jurisdiction (in the Netherlands and Luxembourg, the activity of holding jurisdictions has attracted additional funds into the economy, but the countries themselves have become the world’s biggest investors)
The most widely-spread variants of using offshore companies:
1) For legal persons:
• using offshore territories in import-export operations;
• working on foreign financial and stock markets;
•active work at the equity market;
• loaning from an offshore company;
• transferring profit to an offshore company under a contract to provide information and consultancy services
2) For individuals:
• deposit money;
• accumulation of cash assets;
• the registration of real estate for a foreign company or its subsidiaries
Below on the world map the location of offshore jurisdictions is given. As it is seen from the picture (offshore territories are highlighted in pink colour) the largest accumulation of offshore territories is located in the district of Caribbean Sea, French Polynesia and Western Europe. This arrangement is due to historical background. Most of the zones belong to the former and still existing British and French colonies.
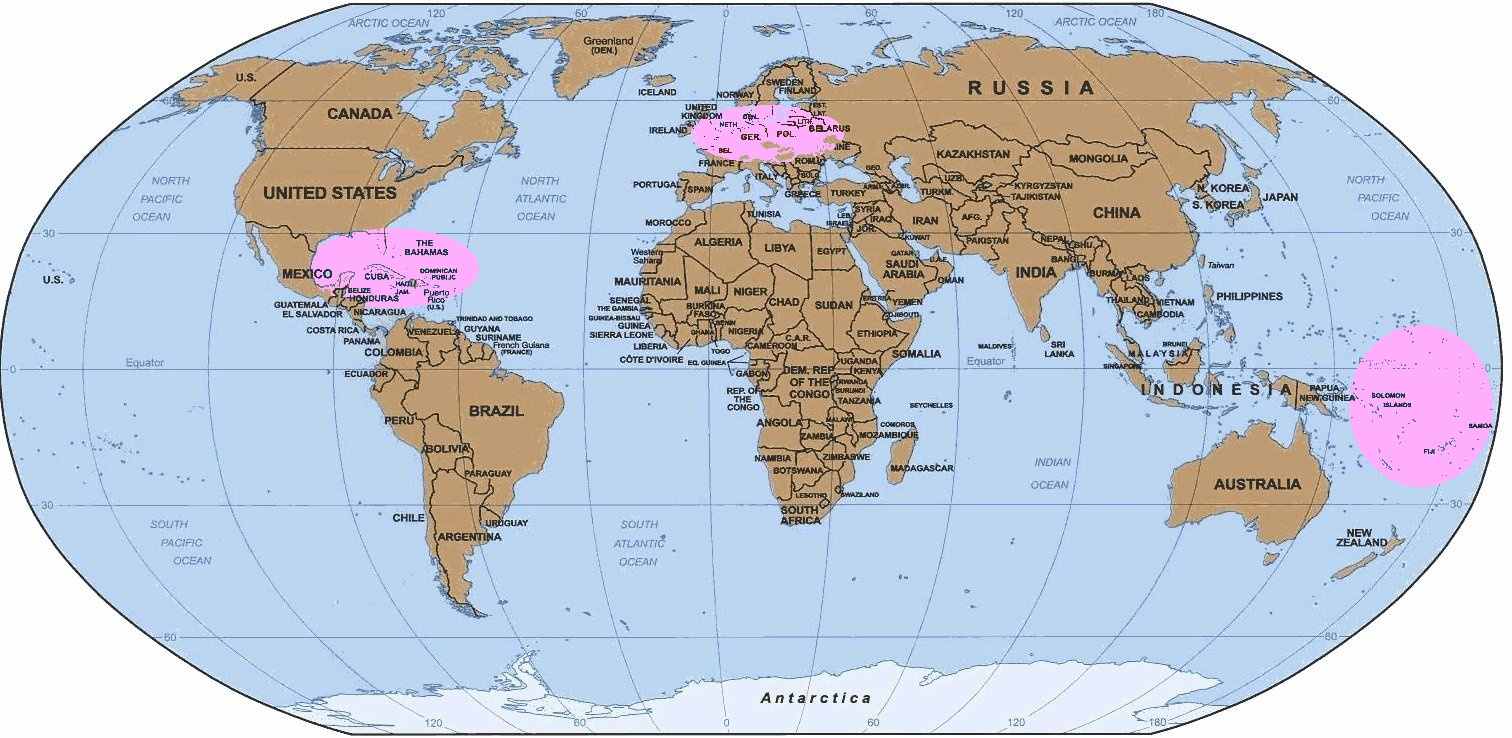
The offshore territories can be classified into three main groups:
| 1 | Classic offshore territories. Countries which allow the offshore companies registered in them and which do not act on their territory, full exemption from taxes in exchange for a small fixed annual fee; these countries do not require to keep accounting records. | Bahamas, British Virgin islands (BVI), Belize, Mauritius, Nevis, Panama, Seychelles Islands, Turks and Caicos. |
| 2 | Countries that have low tax rates for certain types of companies or where such companies can receive significant tax benefits. As a rule, these states require the companies to conduct the accounting records. International community. | Cyprus Hungary, Hong Kong Gibraltar, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Uruguay |
| 3 | Countries that give the companies high respectability and in some cases providing them with, certain tax remissions under strict conditions | USA, UK, Switzerland |
| | | |
Most economists see the positive effect of offshore territories on the global economy which includes:
• Increasing cross-border financial flows;
• Turnover acceleration of financial assets on an international scale
• Creating conditions for investment diversification, improved access to credit and better allocation of capital;
• Motivation to reduce the overall tax burden and on that basis stimulate the economic activity in the global economy;
• Reducing the risk of expropriation and the creation of conditions for the protection of property rights, which, in turn, may initiate increasing of economic growth, especially in donor countries;
• Promotion states prosperity, where offshore companies are located, that promotes more harmonious development of world economy as a whole;
• Improving the competitiveness of companies at the national and global levels using more flexible strategies of developing.
Among the negative aspects of offshore business economists and scientists we mark the following:
• Unfair tax competition, which takes away revenue from offshore countries;
• creating an element of instability in the global economy and finances because of potential savings of large amounts of capital in offshore territories, especially speculative;
• shadow economy support;
• Reduction of the employment in the donor countries;
• providing undue competitive edge to individual companies;
• Adverse impact on the social situation in the donor countries associated with the negative assessment of tax evasion in public opinion.
Comparing these two lists we come to a conclusion that one and the same property of offshore territories can be treated as an advantage and a disadvantage, depending on the specific interests of investors.
Nowadays offshore is very popular in the world, but many companies try to hide their real incomes and, consequently, the economy of states suffers. The offshore territories remain one of the best ways to avoid taxes legally, they help to develop small and medium businesses. However, it should be remembered that the offshore zone is not a way to prosperity. It is expected to raise and strengthen the economy.
